The bubble tea ingredient market has transformed into a sophisticated procurement challenge requiring operators to balance functionality, regulatory compliance, and sensory excellence. As someone who analyzes food science innovations at IFT conferences, I’ve watched this industry shift from commodity sourcing to technical sophistication. You’re no longer just sourcing tapioca pearls—you’re evaluating modified starch systems, shelf-stable formulations, and functional blends that must perform consistently across varying temperature, storage, and preparation conditions. This guide provides a framework for evaluating suppliers based on technical merit rather than price alone.
Understanding the Ingredient Categories
Bubble tea requires five core ingredient systems, each with distinct functional requirements and regulatory considerations.
Tapioca-Based Toppings: Modern tapioca pearl production uses controlled gelatinization processes targeting 60-65 Shore hardness for optimal chewiness. Critical specifications include 85-90% starch content and moisture retention capacity during the 4-hour post-cooking window when pearls must maintain their signature QQ texture. Instant variants use retort sterilization or aseptic packaging to achieve shelf stability without preservatives—request water activity (aw) specifications between 0.85-0.90 for proper moisture control and microbial safety.
Flavoring Syrups: These function as sweetener-flavor carrier systems with 60-70°Brix targets for proper flavor intensity and mouthfeel. The technical challenge is achieving flavor stability across pH ranges (3.5-6.5) while preventing crystallization during cold storage. Clean label formulations use natural preservative systems—combinations of citric acid, potassium sorbate, and modified atmosphere packaging that extend shelf life without sodium benzoate. Premium syrups employ spray-drying or coacervation encapsulation technology to protect volatile flavor compounds from oxidation, resulting in brighter taste profiles that resist degradation.
Powder Systems: Health-positioned powders replace maltodextrin carriers with resistant starch or inulin, achieving 40-60% sugar reduction while maintaining body and mouthfeel. Key specifications: D50 particle size values between 80-120 microns ensure rapid dissolution without clumping, while fat globule size affects perceived creaminess. Sugar substitution introduces processing challenges—erythritol can crystallize during cold storage without proper formulation with stabilizing hydrocolloids like guar gum or xanthan.
Jellies and Textural Toppings: This category involves understanding hydrocolloid interactions. Konjac glucomannan requires alkaline treatment (pH 9-11) for proper gel structure development. Popping boba relies on sodium alginate cross-linking with calcium chloride—specification sheets should show burst strength data (8-12 Newtons) and leakage rates over 90 days to ensure membrane integrity.
Specialty Ingredients: Functional additions like collagen peptides and plant protein isolates require specific molecular weight ranges (2,000-5,000 Daltons for collagen) for bioavailability, while managing native off-flavors through masking systems.

Supplier Evaluation Framework
Technical sourcing requires methodical evaluation beyond taste tests and pricing.
Regulatory Compliance and Documentation
Every supplier should provide GMP certifications, HACCP documentation, and FSSC 22000 for multi-market exports. For U.S. distribution, verify FSVP compliance under FSMA. Request six months of Certificates of Analysis—moisture content variation shouldn’t exceed ±1%, and microbial counts should trend well below limits, not just meet them.
Processing Capability and Quality Systems
Modern ingredient manufacturers maintain controlled processing environments with documented parameters. Spray drying requires inlet temperatures of 160-180°C and outlet temperatures around 80-90°C for proper powder characteristics. Premium suppliers use in-house sensory panels and instrumental analysis (HPLC, rheometers, colorimeters) for batch consistency.
R&D Capacity and Technical Support
Evaluate whether suppliers can function as development partners. Can they reformulate products to meet specific nutritional targets? Customizing formulations for regional preferences requires sophisticated understanding of hurdle technology—combining water activity control, pH management, and modified atmosphere packaging.

Critical Specifications for Each Ingredient Category
When evaluating suppliers, these are the technical specifications that matter most from a food science perspective:
| Ingredient Category | Key Specifications | Target Ranges | Quality Indicators |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tapioca Pearls | Starch content, Shore hardness, moisture retention | 85-90% starch, 60-65 Shore, 4hr texture stability | Consistent gelatinization, minimal syneresis |
| Flavoring Syrups | °Brix, pH stability, flavor retention | 60-70°Brix, pH 3.5-6.5, 90-day stability | No crystallization, bright flavor notes |
| Milk Tea Powders | Particle size (D50), fat content, dissolution rate | 80-120 microns, 20-30% fat, <30sec dissolution | No clumping, smooth mouthfeel |
| Jellies/Toppings | Gel strength, water activity, pH | 300-500 g/cm² (agar), aw 0.90-0.95 | Consistent texture, no syneresis |
| Specialty Ingredients | Molecular weight, bioavailability, solubility | Ingredient-specific | No off-flavors, stable in beverage matrix |
These specifications should appear in technical data sheets, not marketing materials. If a supplier can’t provide quantitative data on these parameters, they’re not operating at a level suitable for serious commercial operations.
Supply Chain Considerations for 2026
Geographic Sourcing: Taiwan leads in technical innovation with decades of R&D investment, while Vietnamese and Thai suppliers offer competitive pricing with improving capabilities. U.S. tariffs add 5-10% to landed costs depending on HTS classification—tapioca typically falls under HTS 1903.
Inventory Strategy: Traditional pearls maintain quality for 12-18 months sealed, instant varieties extend to 24 months. Powders and syrups achieve 12-24 month shelf lives. High-volume operators benefit from quarterly container shipments (1,000-1,500 cases per 40-foot container), while smaller operations should work with regional distributors.
Sustainability and Traceability: Leading suppliers provide cassava sourcing documentation tracing to farm cooperatives, with metrics on water usage and carbon footprint—increasingly important for retail partnerships and consumer perception.
Common Sourcing Pitfalls
Over-Indexing on Price: A 20% savings means nothing if batch inconsistency forces 15% product waste or increases customer complaints. Total cost of ownership includes waste, labor inefficiency, and brand risk.
Ignoring Processing Requirements: Verify preparation protocols match your equipment. Some powder systems need high-shear mixing while others over-emulsify with excessive agitation.
Inadequate Sensory Evaluation: Establish formal protocols comparing samples blind against benchmarks, evaluating sweetness intensity, flavor authenticity, mouthfeel, and aftertaste.
Neglecting Regulatory Due Diligence: Verify flavor systems comply with FDA GRAS status or food additive approvals. Health claims must meet FTC substantiation requirements.
Emerging Ingredient Technologies for 2026
Advanced Texturizing Systems: Next-generation starch modifications using cross-linking or hydroxypropylation allow pearls to maintain texture for 6-8 hours post-cooking rather than 3-4 hours.
Enzymatic Sugar Reduction: Glucoamylase-based systems partially hydrolyze starches into glucose, achieving 30-40% sugar reduction without taste compromises from polyol sweeteners.
Plant-Based Dairy Alternatives: New protein isolation techniques produce cleaner-tasting oat and pea protein bases, while hydrocolloid blending creates convincing fat mimetics approaching sensory parity with dairy.

Building Long-Term Supplier Relationships
Strategic sourcing is relational, not transactional. Establish clear communication protocols for technical issues with direct access to quality teams, not just sales representatives. Consider volume commitments for better pricing and supply guarantees, or negotiate exclusive distribution rights for specific products.
The customization capabilities of your ingredient partner increasingly determine competitive positioning. Can they develop signature flavors exclusive to your brand? Will they adjust formulations for regional preferences?
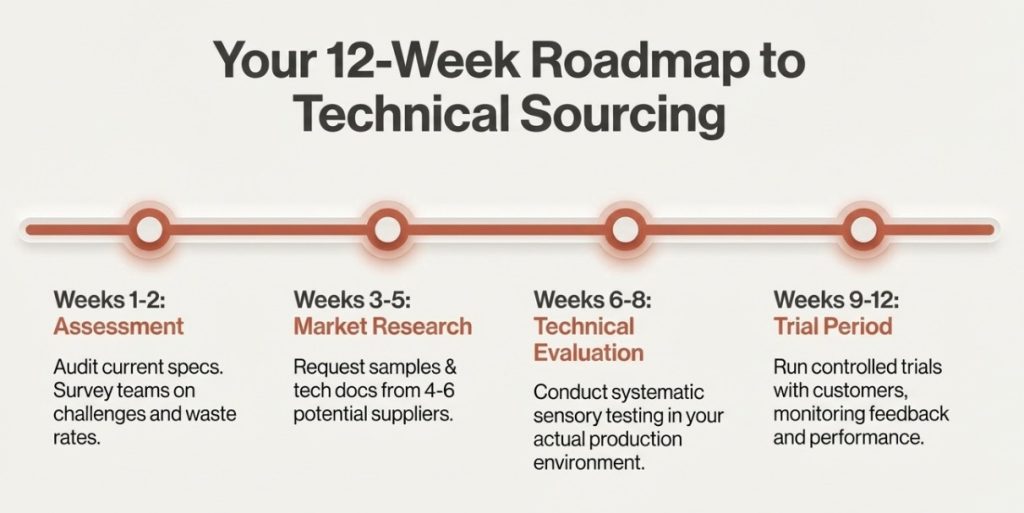
Practical Implementation Steps
Phase 1 – Assessment (Weeks 1-2): Audit current specifications and supplier documentation. Survey operations teams on ingredient-related challenges—preparation difficulties, waste rates, customer feedback patterns.
Phase 2 – Market Research (Weeks 3-5): Request samples and technical documentation from 4-6 potential suppliers. The FAQ section should address technical questions, not just commercial terms.
Phase 3 – Technical Evaluation (Weeks 6-8): Conduct systematic sensory evaluation and test ingredients in actual production environments. Find the optimal match for your operational context and brand positioning.
Phase 4 – Trial Period (Weeks 9-12): Run controlled trials with actual customers, monitoring waste rates, preparation time, holding capacity, and qualitative feedback.
The Path Forward
Ingredient sourcing sophistication will only increase as the bubble tea market matures. Operators who approach procurement with technical rigor build sustainable competitive advantages through superior consistency, innovation capacity, and operational efficiency.
For those opening new operations or expanding existing ones, proper supplier evaluation pays dividends throughout your supply chain. The ingredient decisions you make in 2026 will influence operational costs, product quality, and brand perception for years to come.
FAQ
Premium tapioca pearls require 85-90% starch content, 60-65 Shore hardness, and maintain QQ texture for 4 hours post-cooking. Syrups need 60-70°Brix sweetness with pH 3.5-6.5 stability. Milk tea powders require 80-120 micron particle size, 20-30% fat content, and complete dissolution within 30 seconds. These technical specifications ensure product consistency, operational efficiency, and quality stability for standardized chain operations.
Supplier evaluation requires verifying GMP, HACCP, and FSSC 22000 certifications, requesting 6-month Certificate of Analysis reports to validate batch consistency. Confirm processing capabilities including spray drying and aseptic packaging, plus R&D teams offering formulation customization. Conduct on-site audits of production facilities and quality control processes. Assess technical support capabilities, development partnership potential, and supply chain stability for long-term quality assurance.
Essential certifications include GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices), HACCP (Hazard Analysis), and FSSC 22000 (Food Safety System Certification). U.S. market requires FSVP compliance under FSMA regulations. Suppliers must provide complete traceability documentation, regular testing reports, and allergen declarations. Halal or Kosher certifications expand target market reach. ISO 22000 and BRC certifications represent higher quality management standards ensuring regulatory compliance and consumer safety.
Five core ingredient systems: tapioca-based toppings (pearls, taro balls), flavoring syrups, milk tea powder systems, jelly textural toppings (nata de coco, konjac), and specialty functional ingredients (collagen peptides, plant proteins). Each category has distinct functional requirements and regulatory considerations. Modern formulations emphasize clean label, sugar reduction, and plant-based options. These systems create complete beverage experiences meeting diverse consumer preferences and operational needs.
Traditional tapioca pearls maintain quality for 12-18 months sealed, while instant varieties extend to 24 months shelf life. Syrups and powder systems achieve 12-24 month stability under proper storage conditions. After opening, refrigeration is required with usage within specified timeframes. High-volume operators benefit from quarterly container shipments (1,000-1,500 cases per 40-foot container). Smaller operations should work with regional distributors to avoid inventory pressure and quality degradation risks.
Sources & References
- Cornell Food Science Department — Modified starch functionality and processing parameters
- UC Davis Food Science & Technology — Hydrocolloid systems and texture analysis
- MIT Food & Agriculture Research — Supply chain sustainability metrics
- USDA Economic Research Service — Global cassava production and trade data
- FDA Food Safety Modernization Act — Regulatory compliance requirements
- Institute of Food Technologists — Ingredient innovation and food technology standards
About the Author
Dr. Sarah Chen is a Senior Food Scientist at YenChuan, specializing in carbohydrate chemistry and beverage formulation. With a Ph.D. in Food Science from Cornell University and 12 years in ingredient development, she brings deep technical expertise to bubble tea supply chain optimization. Sarah believes that the future of bubble tea lies not in following trends, but in understanding the fundamental food science that makes great ingredients perform consistently at scale—a philosophy that drives her approach to supplier evaluation and formulation development.
Connect with YenChuan’s technical team on LinkedIn.
Ready to Elevate Your Bubble Tea Ingredient Sourcing?
Whether you’re launching a new concept or optimizing an existing supply chain, partnering with ingredient suppliers who understand food science fundamentals makes all the difference. YenChuan has been developing premium bubble tea ingredients since 1999—from our technical-grade tapioca systems to custom formulation services that address specific functional requirements.
Our team of food scientists and beverage technologists works directly with operators to solve complex sourcing challenges, from clean label reformulations to shelf-stable system development. We don’t just sell ingredients; we provide technical partnership for businesses serious about product quality and operational efficiency.

Let’s discuss how we can support your ingredient procurement strategy. Book a consultation with our technical team →
